Design of Dimeric Bile Acid Derivatives as Potent and Selective Human NTCP Inhibitors
Yang Liu, Lei Zhang, Huan Yan, Zhiqiang Wang, Guoliang Sun, Xiao Song, Zhongmin Zhou,Bo Peng, Liwei Yan, Qingcui Wu, Wenhui Li*, and Xiangbing Qi*
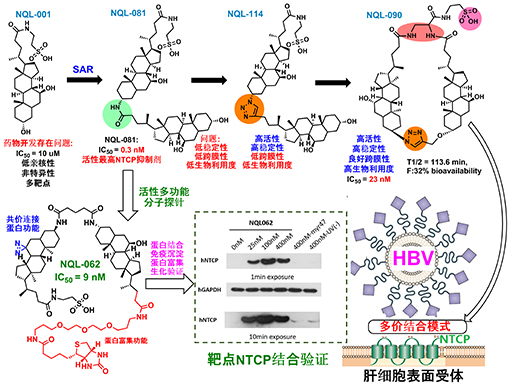
Dimeric bile acid derivatives (DBADs) were developed and tested for their anti-HBV and anti-HDV activities as sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) inhibitors. DBADs exhibited strong and persistent potency of NTCP inhibition, whereas diverse linkers and constitutions showed distinct inhibition features. Motif aa157-165 on NTCP was shown to be a possible binding site of DBADs; therefore, we determined DBADs’ selectivity among NTCPs from different species. A cyclized DBAD scaffold DBA-41 exhibited a high affinity to human NTCP (hNTCP). Intraperitoneal administration of DBA-41 to hNTCP-tg mice induced serum total bile acid elevation. DBA-41 may serve as a biological tool to study NTCP physiological function.