In Silico Identification of a Novel Hinge-Binding Scaffold for Kinase Inhibitor Discovery
Yanli Wang, Yuze Sun, Ran Cao, Dan Liu, Yuting Xie, Li Li, Xiangbing Qi*, and Niu Huang*
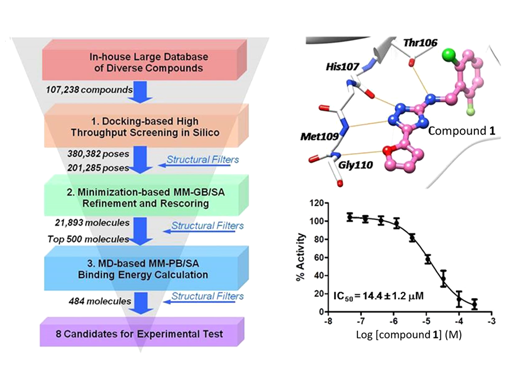
To explore novel kinase hinge-binding scaffolds, we carried out structure-based virtual screening against p38αMAPK as a model system. With the assistance of developed kinase-specific structural filters, we identify a novel lead compoundthat selectively inhibits a panel of kinases with threonine as the gatekeeper residue, including BTK and LCK. These kinases playimportant roles in lymphocyte activation, which encouraged us to design novel kinase inhibitors as drug candidates forameliorating inflammatory diseases and cancers. Therefore, we chemically modified our substituted triazole-class lead compoundto improve the binding affinity and selectivity via a “minimal decoration” strategy, which resulted in potent and selective kinaseinhibitors against LCK (18 nM) and BTK (8 nM). Subsequent crystallographic experiments validated our design. Theserationally designed compounds exhibit potent on-target inhibition against BTK in B cells or LCK in T cells, respectively. Ourwork demonstrates that structure-based virtual screening can be applied to facilitate the development of novel chemical entities incrowded chemical space in the field of kinase inhibitor discovery.